Importance of Vitamin D in inflammation mitigation
Vitamin D (25(OH)D3 and 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol) is avital enzyme for immune defense.
It plays role in calcium uptake, bone metabolism, mineral homeostasis, modulation of the innate and adaptive immune systems and the regulation of cell proliferation, among other functions.
Vitamin D deficiency (serum level below 30-40ng/mL) can lead to cancers, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune conditions, and infections. Its antiproliferative, antifibrotic, immunomodulatory, anti-estrogenic are being recognized.
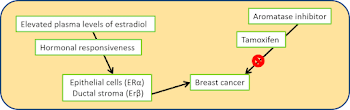
Vitamin D is likely to be a signaling molecule, like estrogen. In fact, both VDR and estrogen receptors share the same protein domains i.e. ZnF (a zinc finger domain) and HOLI (ligand binding domain of hormone receptors). Also, like a CYP enzyme member aromatase, is responsible for conversion of androgen into estrogen, other CYP enzymes are responsible for generating the active form of vitamin D.
Vitamin D is more than a vitamin. Its a hormone with anabolic switch properties. Its level drops when inflammasomes are activated. If vitamin D level can be increased, it can lower the adverse effects of estrogen dominance. Since, estrogen dominance leads to inflammation and a gamut of pathologies, it can be a significant prophylaxis and therapeutic strategies.
For more information, please read: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2452014418300669




Comments
Post a Comment