Estrogen is more than a female sex hormone
Estrogen is a key hormone in both genders, though predominant in the females.
When aromatase enzyme (cytochromes P450) acts on androgen (C19), estrogen (C18) is formed.
Estrogen is critical player in glucose homeostasis, immune defense, bone health, cardiovascular health, fertility, and neural functions.
Estrogen imbalance can cause pathologies ranging from infectious, autoimmune, metabolic to degenerative.
Aging depletes estrogen level, causing bone, muscle, neural degeneration.
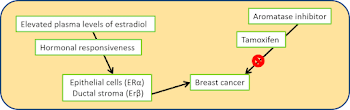
The increasing exposure to inflammatory agents is fueling ‘estrogen dominance’. The encounter to excess estrogen mimics or xeno-estrogens, is inducing the overexpression of estrogen receptors (ERa and ERß). This overabundance of ER receptors is causing metabolic, autoimmune diseases, and cancers. The diseases like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, breast cancer, ovary cancer, and gynecomastia, osteoporosis are direct result of estrogen imbalance. Apart from that, gastric cancer, pituitary cancer, Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, male hypogonadism, transgender issues are linked to aromatase. Hormonal replacement therapy (HRT) is a common therapeutic options for the gamut of diseases, but its not side-effect-free.
Estrogen receptors (ER) occur in the nucleus, cytoplasm, and mitochondria of cells. In silico analysis of the ERs from both types showed the common domains/ motifs i.e. N-terminal DNA binding domain and C-terminal ligand binding domain. Both ERa and ERß receptors have zinc finger (Znf) domains, a small DNA-binding motif. Another oft-occurring domain in these ERs include HOLI, a ligand binding domain.
In silico analyses have shown that androgen receptor, glucocorticoid receptor, thyroid hormone receptor, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor share the same motifs. The antagonistic functions of ERa and ERß have been documented., ERa is the main regulator of GLUT4 (glucose transporter type 4) expression in adipose tissues, which ERß is the repressor. ERa induced leptin expression while ERß inhibited its expression in adipocytes. ERa overexpression is a hallmark of estrogen +ve breast cancer while polymorphism in ERß has been associated with endometrioid carcinoma.
Perturbation in the estrogen levels, the ‘estrogen dominance’ is responsible for the ER expression and activation fluctuations.
 |
So, estrogen is more than a sex hormone in the females. Its a versatile hormone, for both genders, critical to functioning of all aspects of our lives. Hence, its important to not perturb its balance, which can be achieved by keeping inflammatory agents at bay.
More information can be found at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29573619/



Comments
Post a Comment